IoT Monitoring: How It Works, Key Benefits & Use Cases
-
January 17, 2025
-
10 min read

What Is IoT Monitoring and How Does It Work? A Complete Guide
The Internet of Things (IoT) has changed how industries collect, analyse, and act on data. In today’s connected world, millions of devices transmit information every second, supporting applications from smart factories and connected vehicles to energy grids and logistics.
To make sense of this vast network, businesses use IoT monitoring; a real-time process that tracks device performance, network health, and operational data through centralised dashboards.
This guide explains what IoT monitoring is, how it works, the metrics to track, and how solutions like Airtel IoT Hub enable enterprises to manage devices and automation at scale.
Understanding IoT Monitoring
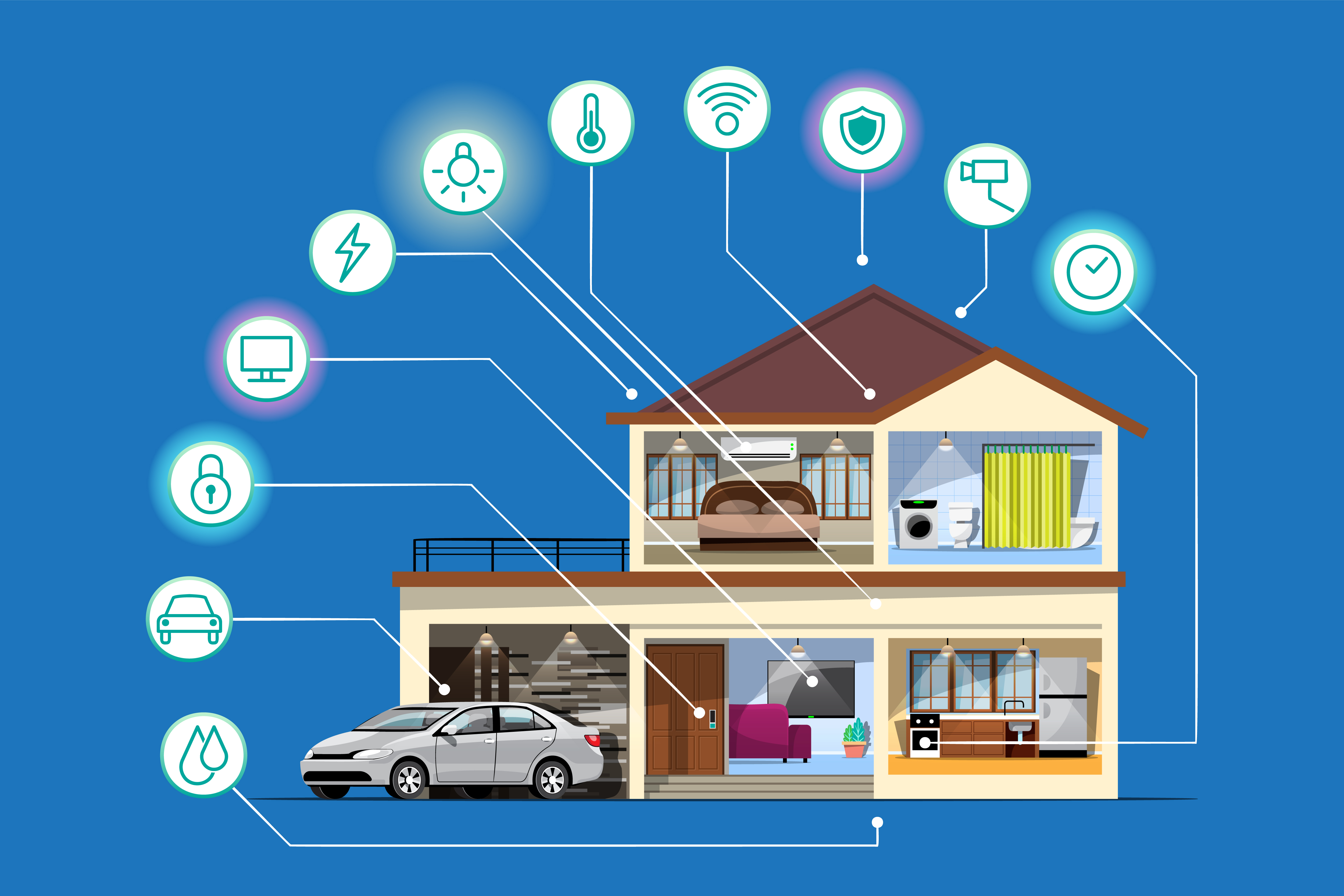
IoT monitoring means observing, collecting, and managing data from connected devices, sensors, and gateways in real time. It forms the foundation of every IoT system by helping businesses identify performance trends, detect faults, and take action instantly.
Unlike traditional monitoring tools designed for servers or desktops, an IoT monitoring platform manages distributed and dynamic environments; often spread across geographies. It monitors everything from hardware health and data throughput to battery levels and network connectivity.
An IoT monitoring platform connects devices to the cloud, where continuous analysis helps in predictive maintenance, real-time alerts, and decision-making. Whether tracking vehicle telematics or industrial machinery, it provides full visibility of connected assets.
Core purposes of IoT monitoring include:
-
Tracking device uptime, connectivity, and performance.
-
Analysing live data streams from sensors and gateways.
-
Detecting anomalies and sending real-time alerts.
-
Supporting remote monitoring IoT for dispersed assets.
-
Powering automation and AI-driven responses.
How IoT Monitoring Works: A Simple 3-Step Process
Modern IoT monitoring platforms follow a three-stage process that converts raw device data into actionable insights. These steps also align with the best practices for managing IoT devices over the internet, where continuous data flow and cloud integration form the backbone of connected operations.
1. Data Collection
The first step in IoT monitoring begins at the device level. Sensors, machines, or vehicles generate continuous data; temperature readings, speed, energy use, or environmental parameters.
This data travels through gateways using wireless technologies such as Wi-Fi, 4G, NB-IoT, or 5G. Platforms like Airtel IoT Connectivity offer multi-network support that keeps these devices online, even in remote areas.
Here, data is gathered from:
-
Embedded sensors and actuators
-
Edge gateways and modems
-
Cellular or satellite connections
-
Bluetooth or LPWAN networks
Each device transmits data packets securely to the cloud for analysis.
2. Cloud Processing & Analysis
Once data reaches the cloud, it moves through several analytic layers. The IoT monitoring platform processes and structures the incoming streams. Machine learning algorithms identify usage patterns, predict failures, and help in predictive maintenance.
During this stage:
-
Raw data converts into meaningful metrics.
-
Alerts are generated for unusual readings.
-
Predictive models analyse equipment health.
-
Dashboards receive updates in real time.
Platforms such as Airtel IoT Hub perform these tasks with speed and accuracy. They manage the lifecycle of each device, track data usage, and automate diagnostics, creating a foundation for intelligent IoT remote monitoring solutions.
3. Dashboard Visualisation, Network Latency & Automated Actions
The final stage focuses on visibility and control. The IoT monitoring dashboard displays live status reports; battery life, signal strength, and device uptime. It also executes automated actions when an anomaly appears, such as restarting a connection, sending a technician alert, or triggering a maintenance workflow.
Features often include:
-
Real-time data charts and heatmaps
-
Network latency and throughput monitoring
-
Custom alerts for device malfunctions
-
Integration with automation tools or APIs
Through automation, remote monitoring IoT becomes proactive, not reactive. Businesses act before downtime occurs, reducing cost and improving reliability.
The Three-Step IoT Monitoring Cycle (Operational View)
Operationally, every IoT monitoring platform follows a repeatable three-step cycle. This cycle maintains the health of connected systems while enabling automation at scale.
1. Device Discovery & Registration
When a new device joins the network, it registers itself with the IoT monitoring platform. During this step, administrators verify its identity, location, and configuration. Platforms such as Airtel IoT Hub use secure APIs and SIM-based registration to connect thousands of devices automatically.
Activities include:
-
Assigning device IDs and security credentials
-
Mapping to location or asset types
-
Activating network and data plans
-
Linking device data to dashboards
2. Continuous Monitoring & Interventions
Once registered, devices start transmitting data. The IoT monitoring system checks connectivity, data throughput, and firmware health continuously. When readings deviate from expected levels, the system intervenes automatically, adjusting configurations or notifying operators.
Examples of continuous monitoring:
-
Real-time vehicle tracking in IoT fleet management
-
Monitoring electricity meters in utilities
-
Analysing production line sensors for quality control
Through such automation, the IoT remote monitoring solution reduces manual work and maintains uptime.
3. Real-Time Alerts, Automation & Actions
In advanced environments, the monitoring cycle concludes with real-time alerts and automatic actions. These responses may involve sending notifications, triggering maintenance requests, or switching to backup connectivity.
For instance:
-
A sudden drop in signal strength triggers a backup SIM profile.
-
Abnormal temperature readings activate cooling systems.
-
High error rates send an instant notification to maintenance teams.
Through this approach, IoT monitoring not only observes devices but also drives operational efficiency.
Key Metrics to Monitor in an IoT System
An IoT monitoring platform tracks several technical metrics that define how efficiently connected devices perform and communicate. Monitoring these parameters helps businesses maintain uptime, detect faults early, and strengthen the performance of remote monitoring IoT deployments.
Essential metrics include:
-
Battery Life – Measures the remaining power in devices or sensors; vital to avoid sudden downtime.
-
Signal Strength / RSSI – Tracks the stability of connectivity between each device and the network; critical for mobile or remote operations.
-
Firmware Status – Indicates software versions and patch updates; keeps devices secure and updated.
-
Error Rates – Identifies system or transmission failures; highlights potential hardware or network problems.
-
Network Latency – Calculates the delay between device and cloud communication; affects responsiveness in real-time analytics.
-
Device Uptime – Shows the total operational time since the last restart; reflects reliability and system consistency.
-
Data Throughput – Measures the volume of data processed per time period; determines how efficiently devices transmit information.
-
Sensor Accuracy – Validates how precise and consistent sensor readings are; supports dependable data-driven decisions.
-
Packet Loss – Represents the percentage of data lost during transmission; impacts data quality and system reliability.
-
Connectivity Health – Evaluates overall SIM and network connection performance; keeps the IoT ecosystem stable and responsive.
By tracking these performance indicators, teams gain real-time visibility, allowing faster action and improved reliability across every IoT remote monitoring solution.
IoT Monitoring Solutions: Architecture & Approaches
The architecture of IoT monitoring platforms varies depending on the scale and type of deployment. Two primary approaches dominate the industry: agent-based and agentless monitoring.
Agent-Based IoT Monitoring
Agent-based monitoring involves installing lightweight software agents within IoT devices or edge nodes. These agents collect operational metrics locally and transmit data to the monitoring platform.
Benefits:
-
Detailed performance data
-
Local analytics and offline data caching
-
Flexible control over device operations
This approach suits industrial environments where machines produce large amounts of telemetry data for predictive maintenance.
Agentless IoT Monitoring
Agentless monitoring removes the need for on-device software. Instead, the IoT monitoring platform communicates directly through APIs, SNMP, or network-level protocols.
Advantages:
-
Easier deployment for large-scale systems
-
Lower device resource usage
-
Simplified maintenance and updates
Agentless approaches are ideal for IoT remote monitoring solutions in logistics, utilities, or smart cities, where thousands of lightweight sensors send periodic updates.
IoT Monitoring in Action: Key Use Cases
IoT monitoring transforms real-world operations by converting device data into actionable insights across industries, from factories and vehicles to energy grids and healthcare systems.
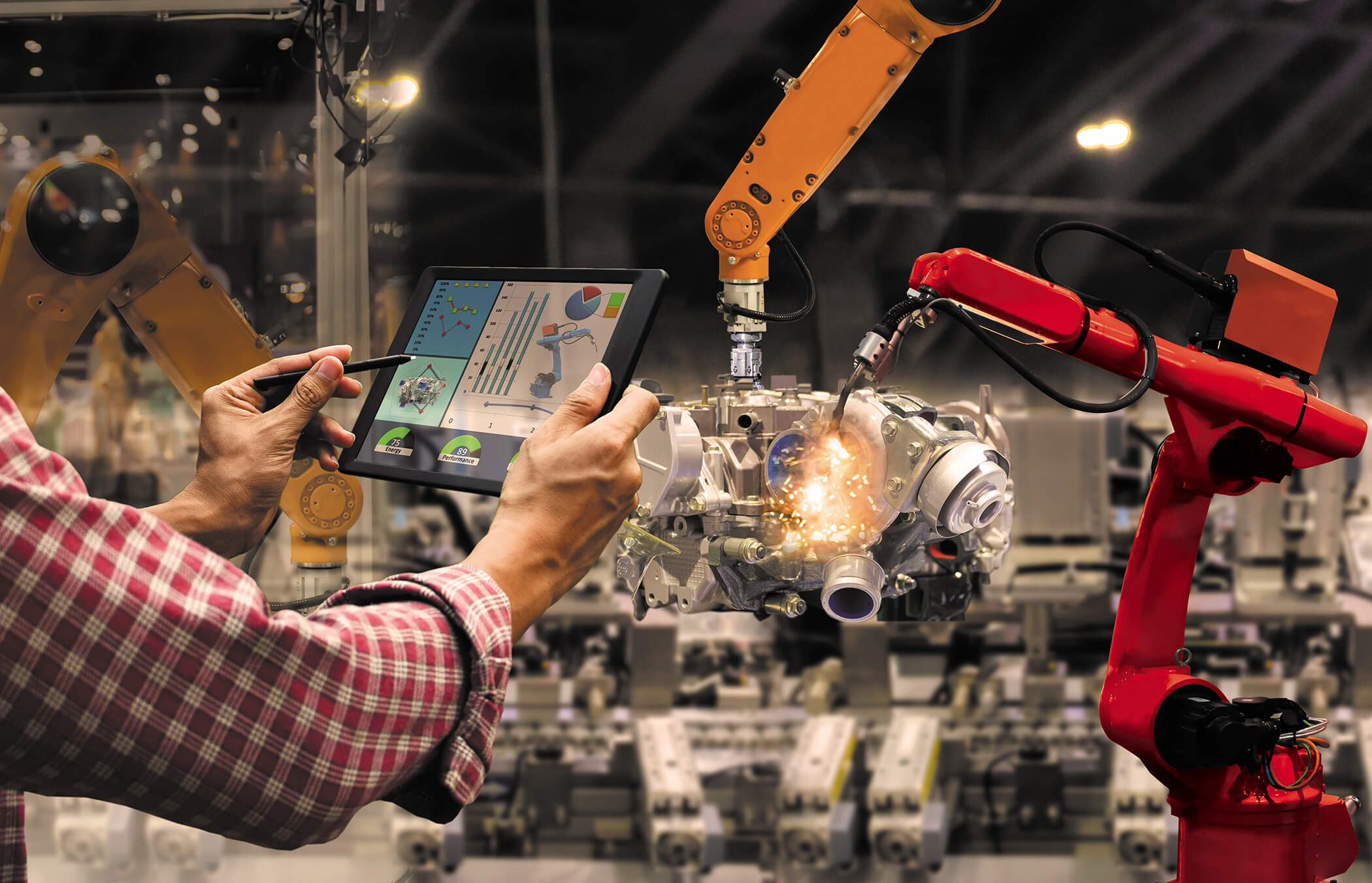
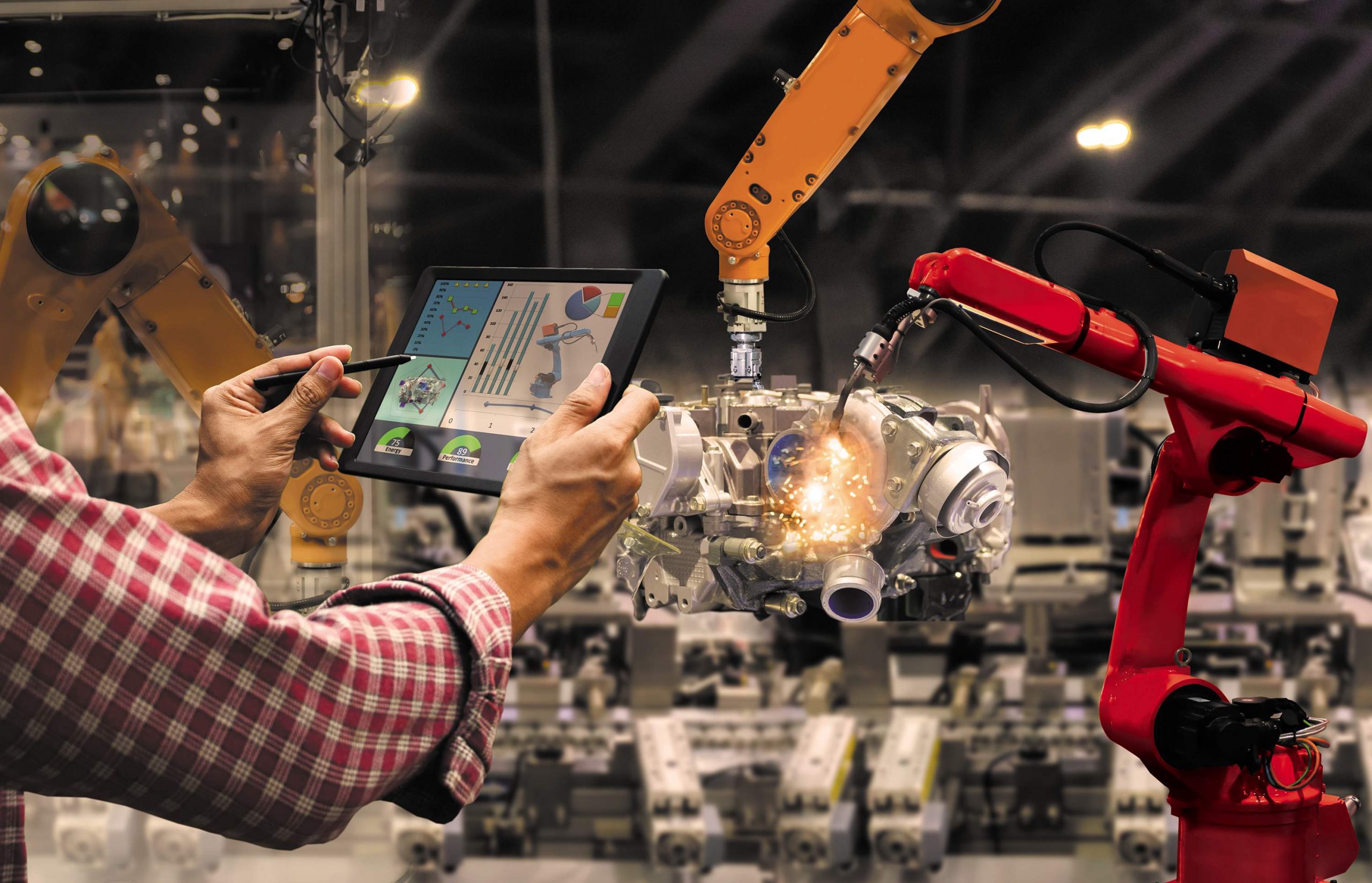
Predictive Maintenance for Industrial Equipment
Industrial machines produce high volumes of sensor data; vibration, pressure, or temperature. With IoT monitoring, these readings feed into predictive models that identify potential failures before they occur.
For example, Airtel IoT Hub enables real-time visibility of connected machines. When vibration exceeds safe limits, the system sends alerts to engineers, allowing preventive maintenance before downtime hits. This IoT remote monitoring solution improves reliability and reduces unplanned repair costs.
IoT Fleet Management & Remote Operations
Fleet operators use IoT fleet management systems to track vehicles, fuel levels, and driver behaviour in real time. Each vehicle transmits data through embedded SIMs, monitored through the Airtel IoT platform.
With features such as:
-
Live route monitoring
-
Driving behaviour analytics
-
Theft or SOS alerts
-
Data-backed fuel optimisation
Remote monitoring IoT enables logistics companies to improve delivery accuracy and reduce operational waste.
Production Control & Quality Monitoring
In manufacturing, IoT monitoring provides end-to-end visibility of production lines. Sensors measure quality parameters, detect irregularities, and automate adjustments.
Benefits include:
-
Real-time defect detection
-
Automated quality adjustments
-
Optimised line efficiency
-
Reduced downtime
By integrating such monitoring with the Airtel IoT Hub, factories achieve consistent output and higher safety levels.
Automated Monitoring Systems
Automated monitoring extends across agriculture, healthcare, and energy sectors. Sensors monitor crop moisture, patient vitals, or power grid stability. The IoT monitoring platform analyses data and executes automated actions like irrigation control or alert generation. This approach converts traditional monitoring into self-operating, data-driven ecosystems.
Airtel IoT Hub: How Airtel Powers Enterprise IoT Monitoring
The Airtel IoT Hub serves as an advanced IoT monitoring platform built for enterprise needs. It supports 5G, NB-IoT, 4G, and 2G networks, providing high scalability and reliable connectivity across industries.
Core capabilities include:
-
Central dashboard to monitor all connected devices.
-
SIM lifecycle management with real-time diagnostics.
-
Multi-cloud integration for flexible deployment.
-
API-driven automation for device provisioning and billing.
-
AI-based insights supporting predictive maintenance and operational intelligence.
-
Secure network access using private APNs.
Through the Airtel IoT Connectivity solution, enterprises connect assets securely and maintain constant visibility, even in remote areas. The platform supports smart metering, connected vehicles, logistics tracking, and industrial automation, forming the digital backbone of modern IoT deployments.
By combining remote monitoring IoT with real-time analytics, Airtel allows enterprises to move from reactive management to proactive decision-making.
Privacy, Security & Device Governance in IoT Monitoring
As IoT ecosystems expand, managing privacy and security becomes vital. Every device acts as a network endpoint, and any breach can compromise the system.
Effective IoT monitoring includes governance mechanisms to manage authentication, data encryption, and access control.
Main security measures include:
-
Encrypted communication between devices and cloud.
-
Role-based access for administrators.
-
Firmware integrity checks.
-
SIM-level authentication.
-
Network segmentation through secure APNs.
Airtel’s IoT infrastructure follows a “secure by design” approach, providing businesses with protected environments for device operations. Governance policies define who accesses which data and when, maintaining operational safety without reducing visibility.
In Summary
IoT monitoring plays a central role in digital transformation. It connects devices, analyses live data, and drives automation across industries. Whether for predictive maintenance, IoT fleet management, or energy monitoring, it empowers enterprises to act faster and smarter.
With Airtel IoT Hub and Airtel IoT Connectivity, businesses gain a robust, secure, and scalable foundation for all their IoT remote monitoring solutions. They can monitor assets globally, reduce downtime, and take instant action through real-time alerts; all within one integrated platform.
In a world where machines communicate as actively as humans, IoT monitoring is not just a technology; it’s the operational nerve centre for a connected future.
 Share
Share