Guide for Businesses to Understand IIoT and its Use Cases
-
May 29, 2022
-
7 min read

The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) stands at the forefront of industrial transformation, ushering in a new era where interconnected devices and systems redefine the boundaries of efficiency, productivity, and innovation. By embedding the advanced capabilities of IoT technology within the core of industrial operations, IIoT is not just an incremental improvement; it’s a paradigm shift that is fundamentally altering the landscape of various sectors, from manufacturing to energy, logistics, and beyond.
This article aims to explore the pivotal role of IIoT in modern businesses, highlighting its critical importance and the profound changes it brings to the industrial realm. With the global IIoT market projected to reach 6.7% from 2023 to 2026, it’s clear that the adoption of IIoT technologies is not just a trend but a strategic imperative for businesses looking to maintain competitiveness and achieve sustainable growth.
Through real-world applications and case studies, we’ll delve into how IIoT is empowering organisations to leapfrog traditional operational challenges, enhance decision-making with data-driven insights, and unlock new opportunities for innovation.
Understanding the Foundation: What Exactly is IIoT?
IIoT refers to the extension and use of the Internet of Things (IoT) in industrial sectors and applications. By connecting machines, devices, and systems across industries, IIoT enables unparalleled levels of information gathering, data analytics, and operational control, fostering an environment where smart machines improve efficiency and productivity.
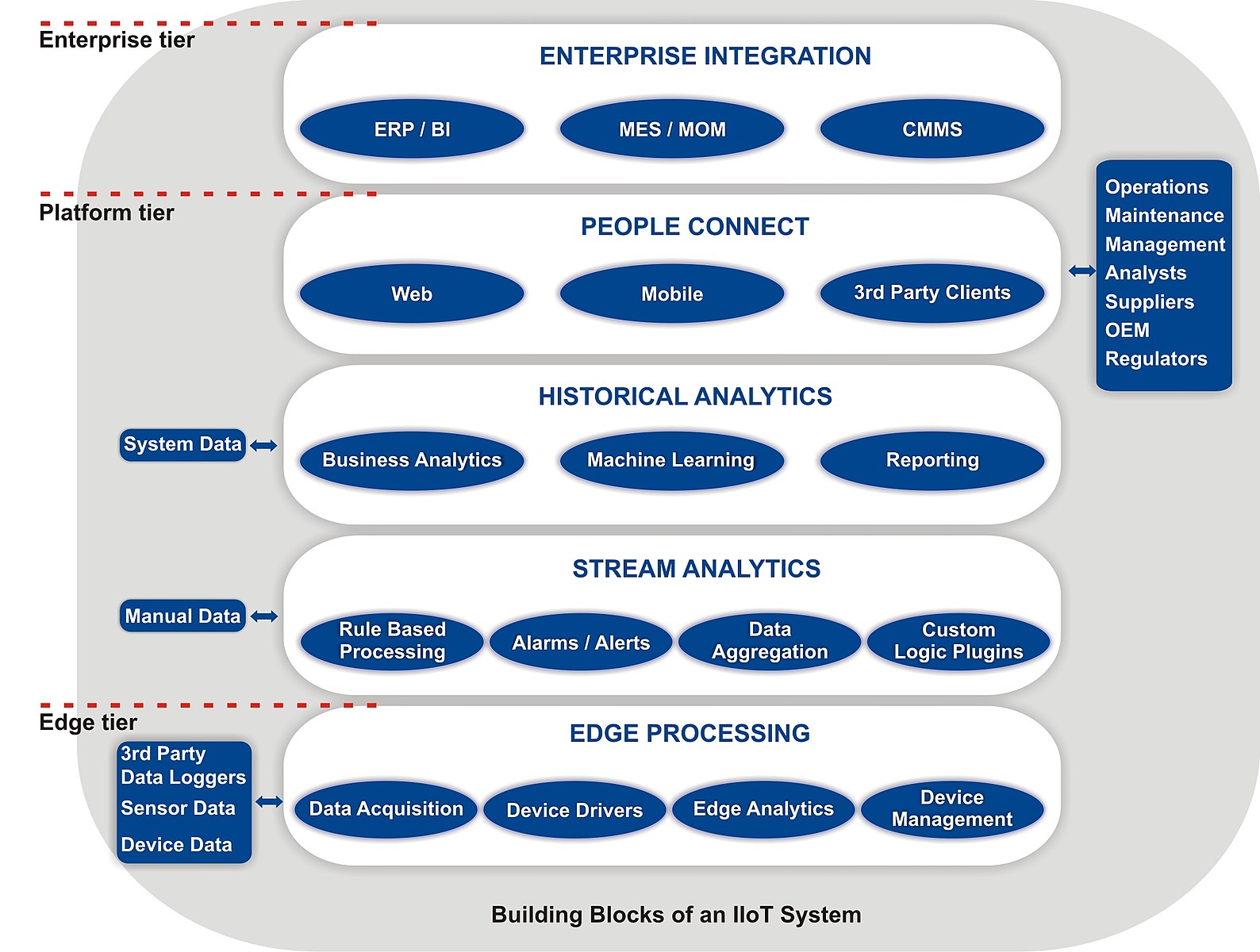
Key Components of IIoT Infrastructure
The Industrial IoT infrastructure is a sophisticated network of interconnected components, each playing a pivotal role in harnessing the full potential of IIoT technology. This infrastructure is the foundation upon which industrial entities can build and deploy smart, data-driven operational processes.
The essential elements of the IIoT infrastructure include:
- Sensors and Devices: These are the frontline instruments in the IIoT architecture, deployed extensively across various points in industrial operations. Sensors and IoT devices are tasked with the critical function of collecting a wide array of data from the environment and machinery.
This data can range from temperature readings and pressure levels to operational speeds and energy consumption rates, providing a comprehensive overview of the industrial ecosystem.
- Connectivity Solutions: Once data is collected, it needs to be transmitted securely and efficiently to central systems for further processing. Connectivity solutions play a crucial role here, acting as the conduits for data transfer.
This IIoT infrastructure component encompasses various technologies, including traditional wired connections, wireless networks, and even advanced satellite communications, ensuring seamless data flow regardless of the industrial setup’s complexity or geographic spread.
- Data Processing and Analytics: The heart of the IIoT infrastructure lies in its ability to transform raw, often voluminous data into meaningful, actionable insights. This transformation is achieved through sophisticated data processing and analytics platforms that employ algorithms, artificial intelligence, and machine learning techniques.
These systems analyse the data to identify trends, patterns, and anomalies, facilitating decision-making processes that are informed, timely, and predictive in nature.
- User Interface: The final component is the user interface, which serves as the bridge between human operators and the IIoT system. Through intuitive dashboards, visualisations, and control panels, operators can interact with the IIoT system, accessing the processed data and analytics to make informed decisions.
The user interface is designed to be user-friendly, enabling operators to easily monitor system performance, adjust parameters, and respond to alerts, ensuring industrial operations’ smooth functioning.
Real-world Applications: Exploring IIoT Use Cases Across Different Sectors
IIoT finds applications across various sectors, demonstrating its versatility:
- Manufacturing: Real-time monitoring of production lines for efficiency.
- Energy: Smart grid technology for improved energy distribution.
- Healthcare: Remote monitoring of patient equipment and conditions.
- Agriculture: Precision farming techniques to optimise crop yields.
Enhancing Efficiency and Productivity: IIoT’s Impact on Manufacturing Processes
The integration of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) into manufacturing operations represents a monumental shift towards higher efficiency and increased productivity. By leveraging advanced IIoT platforms, manufacturers are not only able to monitor equipment performance in real-time but also predict potential failures through maintenance alerts before they disrupt production. This approach significantly enhances operational efficiency and productivity across the board.
For instance, predictive maintenance, powered by IIoT, can decrease unplanned outages by up to 50% and extend the life of an ageing asset by years, according to research from Deloitte.
Moreover, IIoT’s capability to integrate and coordinate diverse production processes transforms the manufacturing workflow, ensuring more efficient operations and faster production cycles.
This seamless integration leads to not only an increase in the overall output but also a substantial enhancement in product quality. For example, a report by McKinsey & Company noted that companies using IIoT technologies to optimise their manufacturing processes have seen operating costs reduced by up to 45%.
Improving Maintenance and Predictive Analytics with IIoT
The transformation of maintenance practices and predictive analytics through the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) marks a significant evolution from the traditional reactive approach to a more insightful, proactive strategy. This shift is not merely conceptual; it’s grounded in measurable outcomes and supported by data-driven studies across various sectors.
A pivotal aspect of IIoT systems is their ability to harness advanced data analytics and machine learning to sift through vast quantities of operational data in real-time. This analytical capability allows for the identification of subtle patterns and anomalies that may indicate impending equipment failures.
According to a report by GE Digital, implementing predictive maintenance powered by IIoT can reduce equipment breakdowns by up to 40%, significantly enhancing operational efficiency.
The longevity of machinery is another critical benefit of IIoT systems. By preempting equipment failures, these systems contribute to extending the operational lifespan of capital assets, maximising the return on investment.
IIoT and Supply Chain Management: Streamlining Operations
The integration of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) into supply chain management marks a significant advancement in how businesses monitor, manage, and optimise their supply chains. This technological infusion enhances operational visibility and accuracy from production through to delivery, transforming traditional supply chain mechanisms into dynamic, efficient systems.
According to research, businesses implementing IIoT solutions in supply chain management could see inventory reductions of up to 90%, substantially lowering holding costs and enhancing cash flow.
Moreover, IIoT’s role in supply chain management extends to improving decision-making processes. With detailed insights into every facet of the supply chain, businesses can optimise operations, reduce waste, and ensure more sustainable practices.
The agility and responsiveness afforded by IIoT technology allow businesses to swiftly adapt to market changes and evolving customer demands, maintaining a vital competitive edge.
Addressing Security Concerns in IIoT Deployments
Addressing security concerns in industrial IoT companies is critical due to the interconnected nature of devices and the sensitivity of the data being processed. The introduction of IIoT expands the attack surface, potentially exposing industrial systems to cyber threats.
To safeguard these systems, businesses need to adopt comprehensive security measures that encompass not only technological solutions like encryption and firewalls but also procedural strategies, including incident response plans and regular vulnerability assessments.
Furthermore, fostering a culture of security awareness through continuous employee training on cybersecurity best practices is essential. By taking a holistic approach to security, businesses can mitigate risks and protect their IIoT infrastructure from potential breaches, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of their data.
Conclusion: The Transformative Potential of IIoT in Industry
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) holds transformative potential for the industrial sector, offering unprecedented opportunities for efficiency, productivity, and innovation.
As businesses continue to explore and implement IIoT solutions, partnering with experienced IoT platform providers like Airtel can offer the expertise, technology, and support needed to navigate this digital transformation successfully.
By embracing IIoT, industries can not only optimise their operations but also pave the way for future advancements and sustainability in the digital age.
 Share
Share