Smart Metering – A Digital Approach of Connected Devices
-
June 14, 2022
-
5 min read
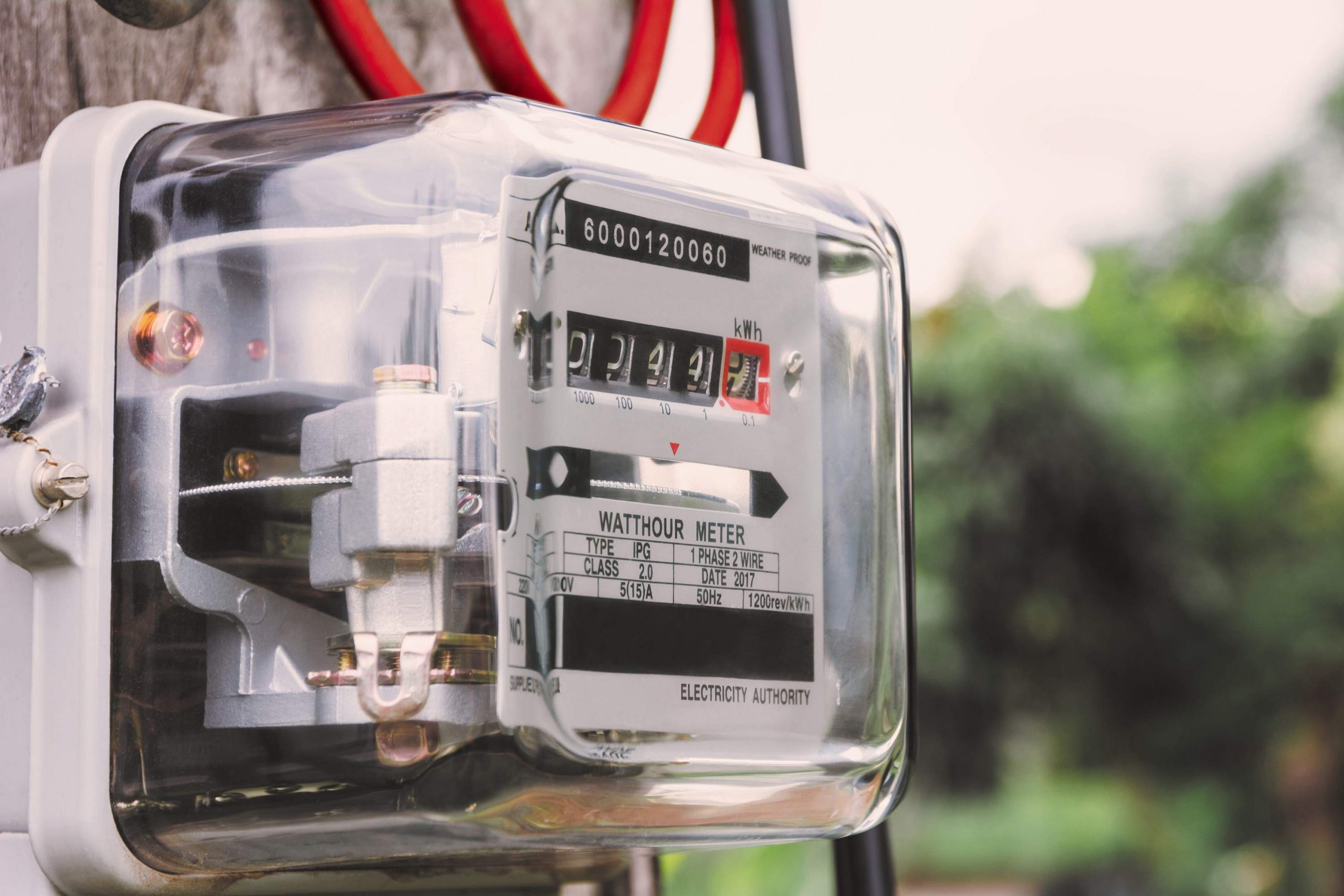
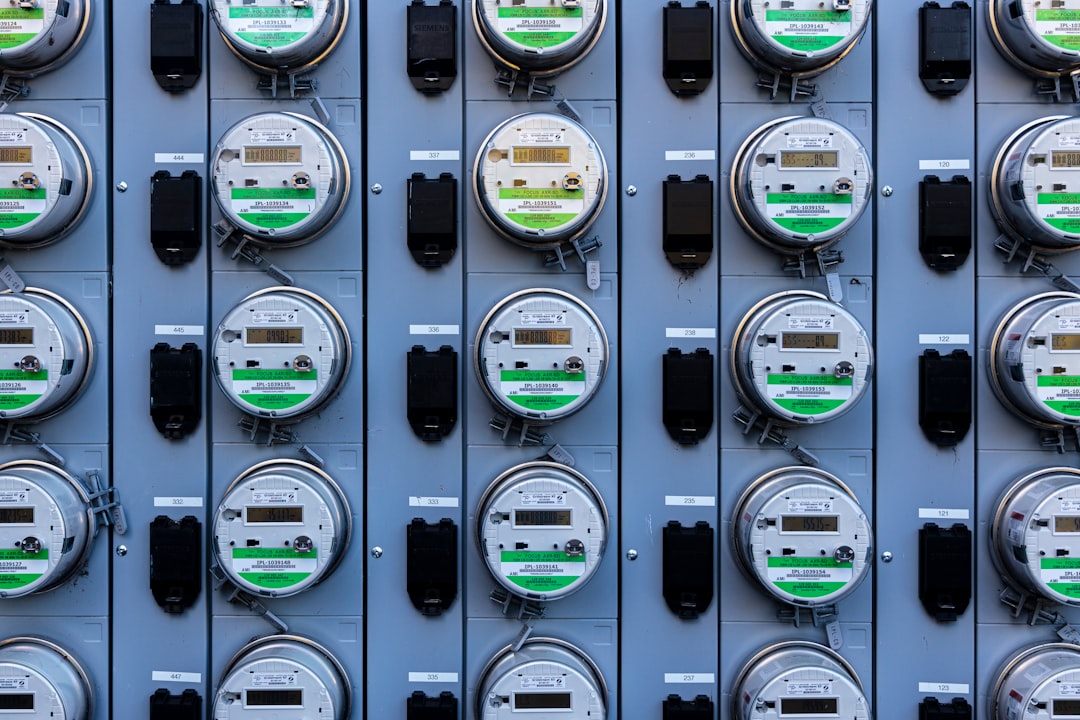
Smart metering is a process that monitors the consumption of resources, such as gas, energy, and water, with the help of sophisticated metering devices that are connected to the Internet using IoT. Smart meters enable the users to know their energy usage in their everyday lives to manage their usage optimally. The significant benefit of the meter is that users get transparent bills based on actual energy usage instead of estimated bills. Smart meters are being used nationwide and internationally.
Compared to the traditional metering systems, smart metering systems use advanced metering infrastructure (AMI). The smart metering systems establish communication with the network via fixed wired connections. For example, a power line carrier (PLC). Few options for wireless communication include Wi-Fi, cellular communication, and Wize.
What is a Smart Meter?
A smart meter is a digital device that communicates remotely with your utility. It sends your resource consumption information to your utility every 15 minutes to an hour.
Apart from informing your energy usage, the smart meter also tells the utility immediately whenever there is a power outage in your area. It quickly dispatches crews to resolve the situation and get back your power supply at the earliest. Once power is back, the smart meter notifies your utility about the resolution.
A smart meter communicates in both directions. The meter transmits information to the utility, and the utility also sends information to the meter without any personnel intervention.
The information sent to the utility includes:
- Detailed usage information
- Voltage monitoring data
- Various alarms
The information sent to the meter includes:
- Pricing information
- Upgrade of meter software
- Date and time
- Disconnect/reconnect instruction
- Programming of meter
- Alarm/load-shed instruction
- Pre-pay information
Smart Meters in India – Types and Applications
Types of smart meters are:
- Three-phase
- Single-phase
- CT-PT
- Transformer operated meter
Application areas:
- Settlement and Billings
- State Estimation of Power Distribution Networks
- Power Quality and Reliability
- Better Customer Service
- Forecast Modeling and Loads Analysis
- Energy Saving
- Balancing Power Generation and Consumption
- Improved Efficiency and Competitive Edge
- Subsidiary Service Support
- Research Support
- Remote Monitoring to Establish Virtual Power Plant
- Security
Smart Meters – Benefits and Challenges
Benefits
- Accurate information on consumption to customers
- Real-time energy recordings and regular consumption reporting.
- Load data collection for evaluating the demand, load forecasting, planning, and tariffing.
- Automation of distribution and monitoring supply quality.
- Top up more easily.
- Lower carbon footprint.
- Improved customer service.
- Shape the company’s infrastructure.
- No hassle of submitting meter readings
Challenges
- If you have SMETS1 meter, it may lose smart functionality when you switch suppliers.
- In-Home Display may not be accurate.
- Signal issues in some areas.
- A smart meter alone does not reduce your bills.
- Not all suppliers support smart meters.
- Health hazards due to RF radiation.
Smart Meters Prices in India
A local manufacturer currently sells a smart meter for Rs 6,000 and Rs 7,500.
Click here for detailed prices.
IoT and Smart Meters
In this advanced era where we depend mostly on IoT platforms, smart meters pave the way for modernized and advanced smart metering solutions. Such metering solutions can remotely monitor, alert, and provide powerful solutions to allow companies and individual households to optimize their water, energy, gas, and fuel consumption.
The biggest challenge for companies that implement smart meters is integrating them with their infrastructure. In addition, they often find it challenging to establish personalized smart metering usage in real-time. The right way to overcome this challenge is to use an IoT platform that offers the best solutions and use cases for smart metering. One best advantage of an enterprise-level IoT platform is its capability to process data. It provides a centralized way to gather data from various smart meters and set up a customized dashboard, user alerts, and notifications. Then, it transfers the collected data into various applications and data stores.
The other major advantage is the cost-effectiveness it brings while implementing smart metering. IoT platform lets focus on customizing the smart metering use cases, thereby saving time and minimizing the associated risks of setting up in-house IoT.
Future of Smart Meters
- The global smart meter market is expected to touch $54.34 billion by 2030, a growth of 10.10% CAGR from 2021 to 2030.
- Asia-Pacific region will show the highest CAGR of 10.60% during 2021 – 2030.
- 8 out of 10 smart meter users are happy using them and recommend them to others. This calls providers to have the right operations and supply in place.
- Analytics and the Internet of Things can help companies provide smart energy solutions to customers.
- Access to data, transparent bills, compliance, and performance bring significant opportunities from smart meters.
- The WNS-Utility Week study findings show the prominent role of energy companies as energy advisors in the generation of smart meters.
Summary
- Smart metering is a process that monitors the consumption of resources, such as gas, energy, and water, with the help of sophisticated metering devices that are connected to the Internet using IoT.
- Types of smart meters include single-phase, 3-phase, CT-PT meter, and distribution transformer operated meter.
- Accurate information on consumption to customers, Real-time energy recordings, and regular consumption reporting are the main benefits of smart meters.
- In-Home Display may not be accurate, and signal issues are the major disadvantages in some areas.
- The global smart meter market is expected to touch $54.34 billion by 2030, a growth of 10.10% CAGR from 2021 to 2030.
 Share
Share







