What is DSL? How it Works, Uses and Benefits
-
November 30, 2022
-
5 min read

In the early days of the “World Wide Web”, or the Web 1.0 as it is called now, your telephone service provider connected you to the web (internet) through “dial-up” service. This service was slow and made your line busy, meaning you could not avail the telephone services when you were connected to the web and vice-versa.
What is DSL?
There was a huge demand for a solution to the painstakingly slow speed of Internet access and unstable connection, and DSL emerged as a revolutionary and innovative technology solution in the 1980s and 1990s.
DSL (Digital Subscriber Line, originally, Digital Subscriber Loop) is a technology where a DSL line is used to connect to the internet and transmit digital data through copper telephone lines. DSL has been one of the most popular ways ISPs (Internet Service Providers) provide DSL broadband or DSL internet connection to the internet users.
There are currently many telecommunication technologies available to give access to internet services and digital information. What makes DSL internet unique is the fact that it uses existing telephone lines/connections, with special adaptations, to connect the internet to the subscribers.
DSL internet operates DSL services over existing telephone lines like the dial-up connections. It brought in a major revolution in the earlier days of the internet by providing much better DSL speed than dial-up.
How does DSL work?
DSL providers bring a network connection into your home or business through telephone lines, allowing you to use the internet and make telephone calls at the same time. This aspect is the main advancement from the dial-up, where you could do only one activity (internet or call) at a time.
It works so because the DSL technology divides the telephone signals into three bands of frequencies. While one band facilitates telephone calls, the other two bands connect you to the internet through the process of uploading and downloading online activity.
DSL companies provide hardware, similar to the cable modem, called a DSL transceiver to its subscribers. This hardware only works for DSL connections, and in many cases only the connections provided by the same ISP.
The modem connected to the computer separates the voice from data (bands) as explained above and as shown in the below diagram. You can also connect Ethernet to DSL to connect your local network to a DSL network.
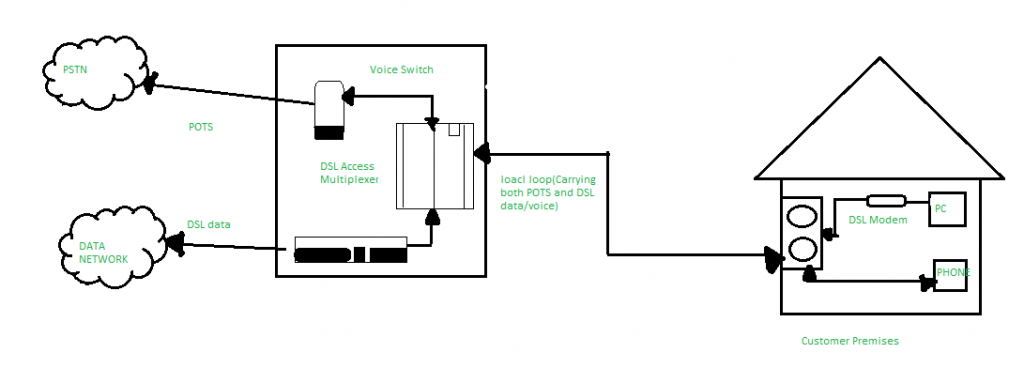
In a DSL network, the telephone lines will run from your wall to the outside to the ISP hub. The DSL cables that are used to send data back and forth are mostly ADSL lines. The Asynchronous DSL means that one side of the line (download) is bigger than the other side (upload). What ADSL does is fast downloads and slow to moderate speed uploads, which is what is commonly in demand.
The two primary types of DSL connections are – asymmetric (ADSL) and symmetric (SDSL) while ADSL is cheaper and more popular because of its faster download speed than upload speed, the download and upload speeds are equal in SDSL, which professionals who have to back up large volumes of data to the cloud and VPN users prefer over ADSL.
One important thing to note here is that the more distant your connection is from the Service Provider hub, the quality and speed of your dial-up connection will be poor. That means the speed and quality of the connections that are closer to the ISP hub will be better.
What are the Advantages of DSL?
We all know that connectivity technologies have advanced beyond DSL in the forms of cable internet and fiber, though DSL is still widely used in many areas. It may take a few more years before DSL will be fully replaced by new technologies, like dial-up was replaced by DSL. Digital lines offer you some advantages, particularly in comparison to dial-up:
- It allows you to make phone calls and connect to internet simultaneously
- It’s faster and provides a consistent and stable internet speed
- You can select the suitable price plan, based on the speed you want
- There is no need for additional wiring as a DSL connection makes use of your existing telephone wiring
- DSL internet is still a very cost-effective option as compared to the other available options
DSL is the ideal choice for those users who use the internet considerably for browsing web, streaming music and videos, accessing online apps like e-commerce sites, and posting on social media platforms at lower cost. One major disadvantage of DSL is that the further you are from the telephone ISP central location or hub, the internet speed will be slower.
Concluding note
DSL Internet service is arguably still the best option by way of good speed for a lower cost, it only works over a certain distance and will not be available in many areas where DSL technology is not supported by the telephone service provider’s infrastructure. If you are using ASDL, it will be for receiving data than it is for sending data over the Internet. Both cable internet and DSL offer similar quality of internet connectivity, but the latter is less expensive.
If you need internet connectivity for your small business or home, you should consider all the available options to understand if dial-up will meet your needs or is it necessary to prefer other expensive options.
 Share
Share









