The Role of IoT Functional Blocks in Smart Operations
-
February 1, 2026
-
4 min read
Understanding IoT Functional Blocks: The Building Blocks Behind Every IoT System
The Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand rapidly, connecting more than 19.8 billion devices globally in 2026. IoT drives automation, efficiency, and innovation across industries, including manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and utilities. Each IoT solution operates through a combination of IoT functional blocks that convert real-world data into digital intelligence.
At the foundation of this structure are IoT sensors and actuators, supported by secure connectivity platforms such as Airtel IoT Connectivity, which enable devices to communicate effectively and drive intelligent decision-making at scale.
Core IoT Functional Blocks
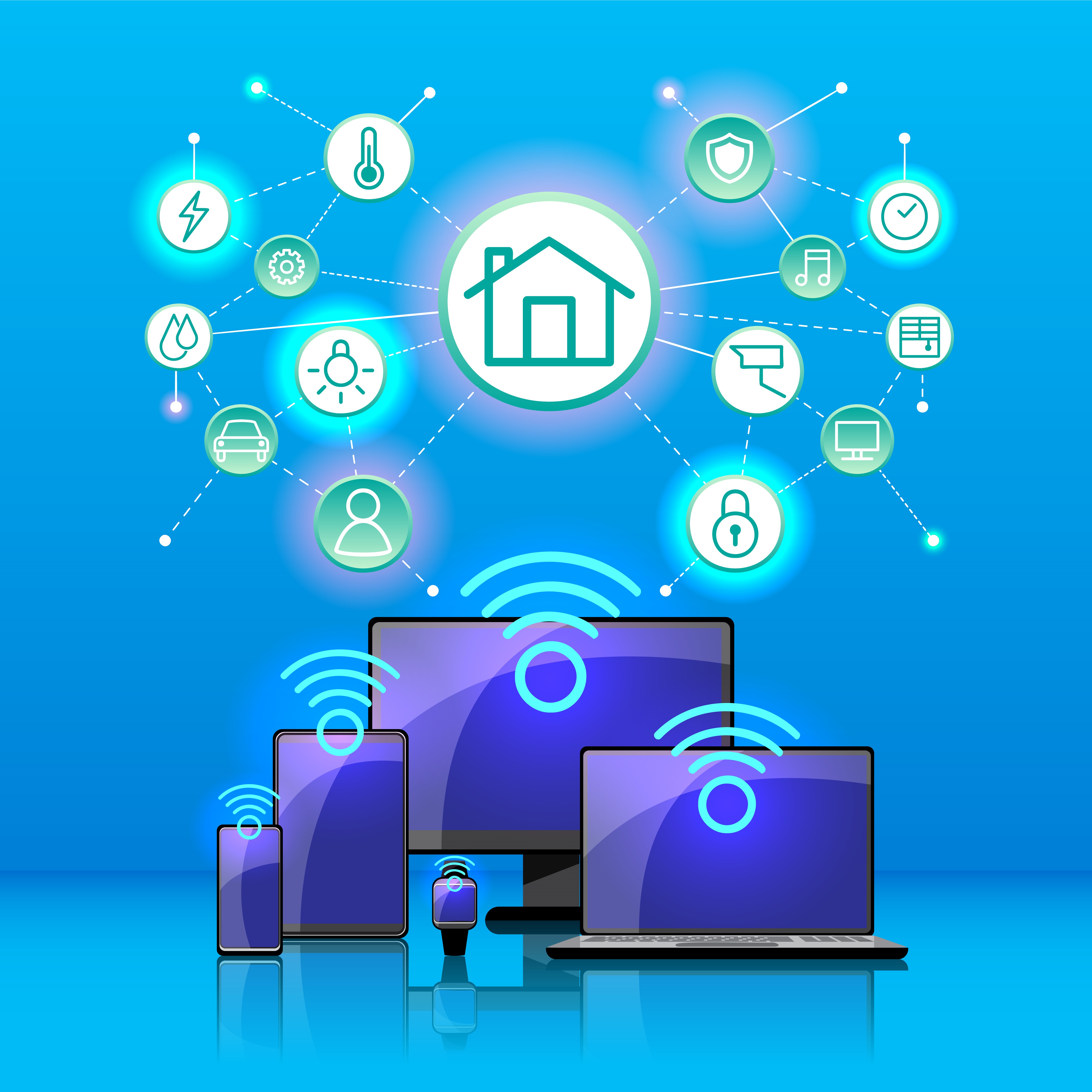
Every IoT ecosystem works through several functional blocks. Each has a clear purpose that supports the data journey from device to application.
|
Functional Block |
Purpose |
Example Use |
|
IoT Sensors and Actuators |
Detect and control physical conditions |
Machine temperature control |
|
Connectivity Layer |
Transmits data across devices |
5G, 4G, NB-IoT |
|
Processing Layer |
Filters and analyses data |
Edge or cloud platforms |
|
Application Layer |
Presents insights to users |
Predictive maintenance dashboards |
These IoT functional blocks create a continuous flow of data. Information is collected, transferred, processed, and displayed for business decisions.
IoT Sensors and Actuators
IoT sensors and actuators form the foundation of every connected system. Sensors measure variables such as heat, motion, pressure, or humidity. Actuators perform actions based on sensor data. They adjust machinery, control lights, or regulate systems automatically.
Key Qualities
-
Accuracy: Delivers precise data for monitoring.
-
Speed: Responds instantly to inputs.
-
Durability: Operates in challenging environments.
-
Scalability: Supports large networks of devices.
Connectivity and Communication
Connectivity enables data to move between devices, gateways, and applications. The choice of network depends on coverage, data rate, and power needs.
|
Technology |
Coverage |
Power Use |
Application |
|
Wi-Fi |
Local |
Medium |
Smart buildings |
|
5G |
Wide |
Moderate |
Real-time control |
|
LoRaWAN |
Long-range |
Low |
Remote monitoring |
|
NB-IoT |
Deep coverage |
Low |
Smart metering |
|
Satellite IoT |
Global |
Moderate |
Maritime operations |
Each option serves specific use cases. Enterprises often combine several for reliability and cost control.
Data Processing and Analytics
Raw data from IoT devices becomes valuable only after processing. The processing layer transforms incoming data into usable insights.
Types of Processing
-
Edge Processing: Occurs near devices for fast reactions.
-
Fog Processing: Occurs at local nodes for mid-level analysis.
-
Cloud Processing: Occurs centrally for deep analytics.
For example, sensors in logistics trucks track cargo temperature. Edge devices send alerts if limits are crossed. Cloud systems later analyse patterns for better planning.
Reliable communication supports this process. Airtel IoT Connectivity provides high-speed, low-latency links for real-time analytics. Its secure network helps protect data during transmission and storage.
Application Layer and Integration
The application layer bridges IoT insights with business operations. It translates processed data into dashboards, alerts, and automated workflows that support faster, data-based decisions.
Industry Use Cases
-
Manufacturing: Enables equipment monitoring and predictive maintenance to reduce downtime.
-
Utilities: Supports real-time energy tracking and automated consumption control.
-
Healthcare: Monitors patient data remotely for timely medical interventions.
-
Transportation: Optimises routes and manages fleet performance through live data.
-
Retail: Uses smart shelves and inventory tracking to enhance efficiency.
This layer transforms raw data into actionable intelligence, driving efficiency, innovation, and operational excellence across industries.
Security and Scalability
Security is vital in any connected environment. Each device introduces potential risks that must be managed carefully.
Main Security Practices
-
Encrypt data during transmission.
-
Authenticate devices regularly.
-
Monitor networks for threats.
-
Update firmware to remove vulnerabilities.
Scalability is equally important. As device numbers grow, management becomes complex. Airtel IoT Connectivity simplifies this with its secure-by-design IoT Hub. Enterprises can track devices, control SIM usage, and manage access from a single interface. The platform’s design supports growth across multiple regions with consistent performance.
This approach allows organisations to expand IoT operations while maintaining control and visibility.
Future Outlook
IoT technology continues to evolve. Emerging trends are shaping how future IoT systems will operate.
-
Edge AI brings faster decision-making at the device level.
-
5G adoption supports real-time automation.
-
Blockchain strengthens data authenticity.
-
Sustainability initiatives use IoT to reduce energy waste.
Enterprises combining strong connectivity and data analytics will gain long-term advantages in performance and reliability.
Key Takeaways
IoT functional blocks define how connected systems operate and deliver value. From IoT sensors and actuators that collect and control data to applications that guide strategy, each layer adds strength. Reliable connectivity keeps this digital structure active and secure.
Organisations seeking advanced connectivity solutions can explore Airtel IoT Connectivity. Its scalable platform, 5G readiness, and intelligent IoT Hub enable enterprises to manage devices efficiently.
Empower your connected operations with Airtel IoT Connectivity and unlock new levels of digital efficiency.
 Share
Share